<h1>How Renewable Energy is Driving Economic Growth Worldwide: A Solar Flare of Opportunity</h1>
<p>The world is undergoing a seismic shift, not of tectonic plates, but of energy sources. Forget the rumbling of coal mines and the gushing of oil wells; the future hums with the quiet efficiency of solar panels, the graceful dance of wind turbines, and the potent energy of geothermal vents. Renewable energy isn't just an environmental imperative; it's the engine of a new global economy, sparking unprecedented growth and redefining prosperity. Let's explore how this "green revolution" is reshaping the economic landscape.</p>
<h2>The Investment Avalanche: Pouring Billions into a Brighter Future</h2>
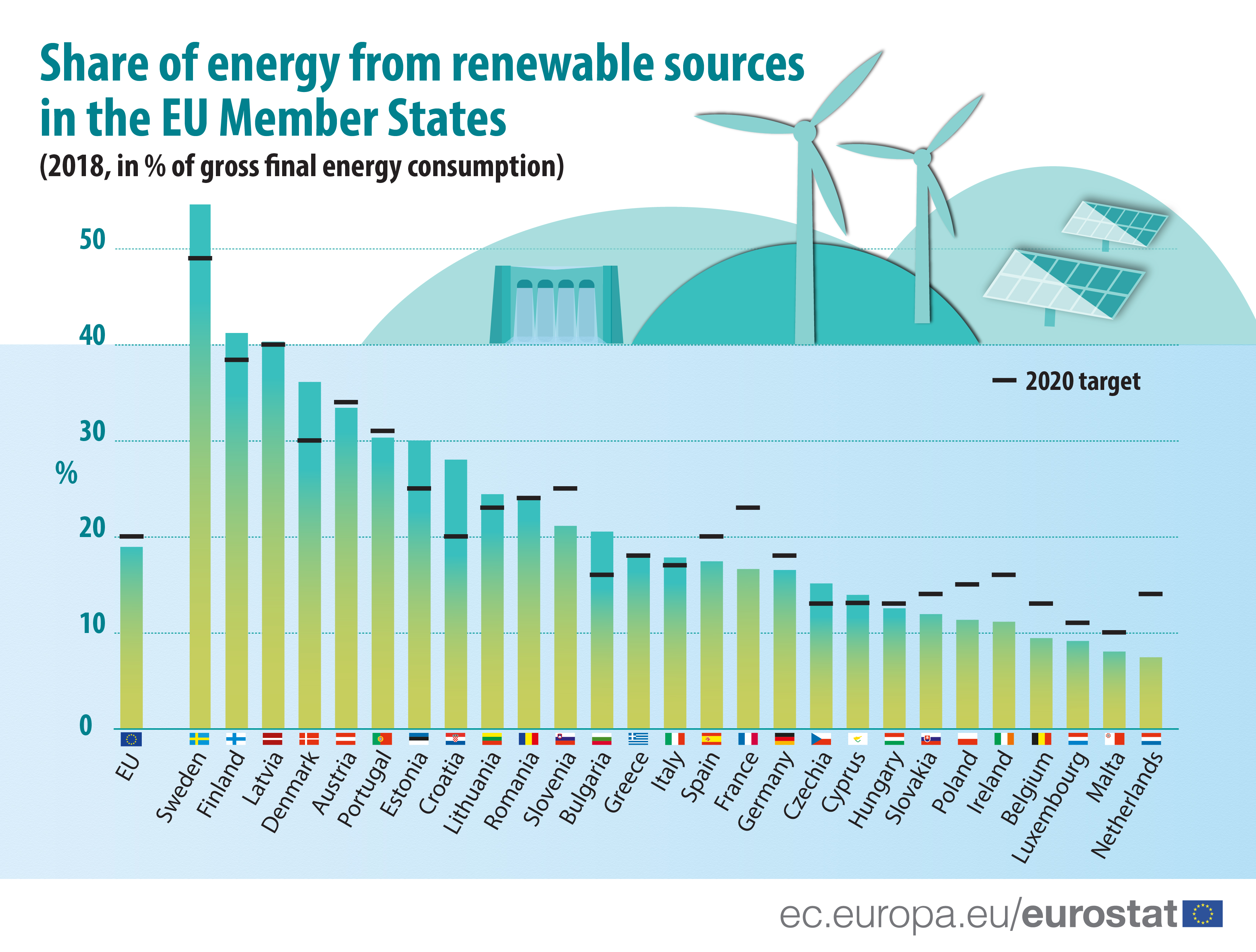
<p>The financial world has woken up to the colossal potential of renewable energy. Investment is pouring in at an astonishing rate, eclipsing fossil fuels in many regions. This isn't just a trend; it's a tidal wave. Governments, private investors, and international organizations are all recognizing the long-term value proposition: a stable, sustainable, and increasingly cost-competitive energy source.</p>
<h3>Investment in Renewable Energy (2022)</h3>
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<th>Sector</th>
<th>Investment (USD Billions)</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Solar</td>
<td>235</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Wind</td>
<td>170</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Hydropower</td>
<td>35</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Other (Geothermal, Bioenergy)</td>
<td>20</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h2>Job Creation: Painting the World Green with Employment</h2>
<p>The transition to renewable energy is not just about generating electricity; it's about creating jobs. Millions of new positions are being generated across the entire value chain, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. These are not just low-skilled jobs; they encompass a wide range of expertise, driving innovation and fostering a new generation of green-collar workers.</p>
<h3>Renewable Energy Employment (Estimated Global, 2023)</h3>
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<th>Sector</th>
<th>Estimated Jobs</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Solar PV</td>
<td>4.3 Million</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Wind</td>
<td>1.7 Million</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Biofuels</td>
<td>1.8 Million</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Hydropower</td>
<td>1.5 Million</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Geothermal</td>
<td>200,000</td>
</tr>
</table>
<h2>Energy Independence: Freedom from the Fossil Fuel Grip</h2>
<p>One of the most significant economic benefits of renewable energy is energy independence. Countries that rely on imported fossil fuels are vulnerable to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability. By diversifying their energy sources and investing in domestic renewables, nations can secure their energy supply, reduce their trade deficits, and boost their economic resilience. Solar, wind, and other renewables offer countries a path toward true energy sovereignty.</p>
<h2>Innovation and Technological Advancements: Fueling the Future</h2>
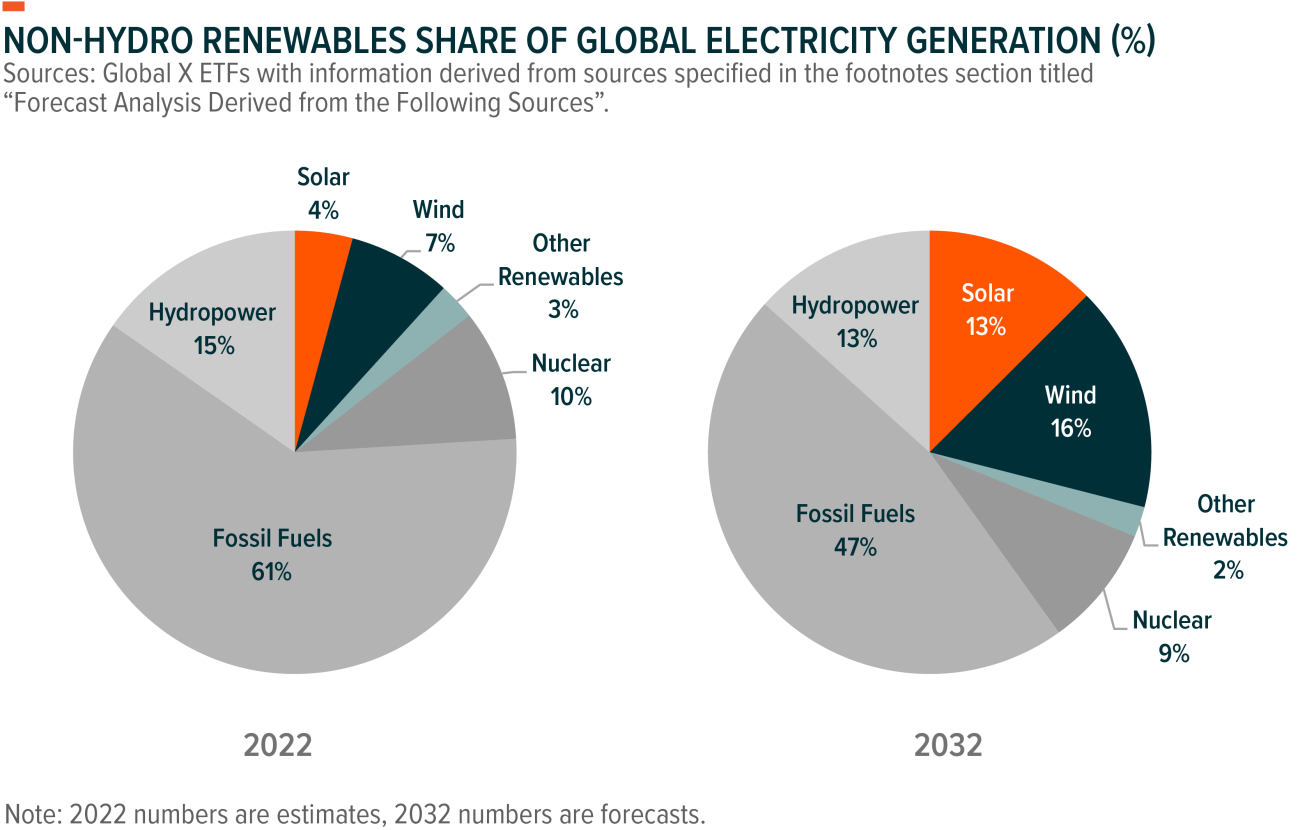
<p>The renewable energy sector is a hotbed of innovation. Continuous advancements in solar panel efficiency, battery storage technology, smart grids, and wind turbine design are driving down costs and improving performance. This innovation cascade is not confined to the energy sector; it spills over into other industries, creating new business opportunities and stimulating overall economic growth. From advanced materials to sophisticated software, renewables are at the forefront of technological progress.</p>
<h2>Reduced Environmental Costs: The Bottom Line Benefit</h2>
<p>While not a direct economic benefit, the environmental advantages of renewable energy translate into significant long-term cost savings. Reduced air pollution leads to lower healthcare expenses and increased worker productivity. Mitigation of climate change reduces the economic impact of extreme weather events. The avoided costs of environmental degradation, often hidden in the traditional economic model, become increasingly apparent as the world shifts towards a cleaner energy future.</p>
<h2>Case Studies: Green Growth in Action</h2>
<p>Let's examine a few shining examples of how renewable energy is fueling economic prosperity:</p>
<ul>
<li><b>Germany:</b> A pioneer in the Energiewende (energy transition), Germany has created hundreds of thousands of jobs in the renewable energy sector and become a global leader in solar and wind technology.</li>
<li><b>China:</b> The world's largest investor in renewable energy, China has transformed its manufacturing sector and is rapidly becoming a dominant force in the global clean energy market.</li>
<li><b>Morocco:</b> The Noor Ouarzazate solar power plant, one of the largest concentrated solar power plants in the world, is a testament to Morocco's commitment to renewable energy and its potential to attract foreign investment and diversify the economy.</li>
</ul>
<h2>Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Transition</h2>
<p>The transition to a renewable energy-driven economy is not without its challenges. These include:</p>
<ul>
<li><b>Intermittency:</b> The fluctuating nature of solar and wind energy requires sophisticated energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies.</li>
<li><b>Infrastructure:</b> Significant investment in transmission infrastructure is necessary to transport renewable energy from production sites to consumers.</li>
<li><b>Policy Support:</b> Clear and consistent government policies are essential to provide investor confidence and accelerate the deployment of renewable energy projects.</li>
</ul>
<p>However, these challenges are also opportunities. Technological breakthroughs, innovative business models, and supportive government policies can overcome these hurdles and unlock even greater economic benefits. The future is bright, and the energy sector is a key contributor.</p>
<h2>Conclusion: Riding the Renewable Energy Wave</h2>
<p>Renewable energy is no longer a niche market; it's the mainstream, a powerful force driving economic growth and reshaping the global landscape. From massive investment flows and job creation to enhanced energy security and environmental benefits, the advantages are undeniable. As we ride the renewable energy wave, we are not just building a cleaner planet; we are building a more prosperous, sustainable, and resilient future for all.</p>
Additional Information
Renewable Energy: Driving Economic Growth Worldwide – A Detailed Analysis
Renewable energy is no longer just an environmental imperative; it’s a powerful engine of economic growth worldwide. Its impact is multifaceted, touching various sectors and creating new opportunities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how:
1. Investment & Job Creation:
- Massive Investment: The renewable energy sector has attracted trillions of dollars in investment globally. This capital infusion spurs innovation, fuels infrastructure development, and supports manufacturing. Examples include:
- Public Funding: Government subsidies, tax incentives, and grants are crucial catalysts, particularly in the early stages of project development. Programs like the US Inflation Reduction Act and various EU initiatives have boosted investment dramatically.
- Private Sector Involvement: Private equity firms, pension funds, and institutional investors are increasingly drawn to the sector’s long-term stability and attractive returns, particularly as the cost of renewables has plummeted.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in renewable energy projects translates directly into construction, manufacturing, and installation jobs. This covers solar farms, wind turbines, hydropower plants, geothermal installations, and bioenergy facilities.
- Job Creation Across the Value Chain:
- Manufacturing: The production of solar panels, wind turbine components, batteries, and other renewable energy equipment generates manufacturing jobs, from raw material extraction to final product assembly. Countries with strong manufacturing capabilities, like China, Germany, and the US, are major beneficiaries.
- Installation & Construction: The deployment of renewable energy projects requires skilled workers for site preparation, installation, grid connection, and maintenance. This creates a significant number of local, often high-paying, jobs in diverse locations.
- Operation & Maintenance: Ongoing operation and maintenance of renewable energy facilities require a specialized workforce, including technicians, engineers, and data analysts.
- Research & Development: Investing in R&D fuels further advancements in renewable energy technologies, creating high-skilled jobs in areas like materials science, engineering, and computer science.
- Supply Chain: Renewable energy projects create opportunities for various supporting industries, including transportation, logistics, and financial services.
- Geographic Distribution of Benefits: While certain countries are leaders in renewable energy production, its economic benefits extend globally. Developing countries with abundant renewable resources can leverage them to attract foreign investment, create local jobs, and diversify their economies.
2. Cost Reductions & Energy Independence:
- Declining Costs: The most significant economic driver is the dramatic cost reduction in renewable energy technologies, particularly solar and wind power. Innovations in manufacturing, economies of scale, and improved efficiency have led to:
- Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Declines: The LCOE, which represents the average cost of electricity generation over the lifetime of a plant, has fallen significantly for renewables. In many regions, solar and wind are now cheaper than fossil fuels, making them increasingly attractive for investors and consumers.
- Grid Parity: Renewable energy sources have achieved grid parity (cost competitiveness with fossil fuels) in numerous locations, even without subsidies.
- Reduced Energy Costs for Consumers & Businesses: Lower electricity costs translate into increased disposable income for households and reduced operating expenses for businesses, leading to greater economic activity and competitiveness.
- Energy Independence & Security: Investing in domestic renewable energy resources reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels, strengthening national energy security and shielding economies from price volatility in global energy markets. This can be particularly beneficial for countries that lack their own fossil fuel resources.
- Improved Trade Balance: By reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports, countries can improve their trade balances and redirect funds to other sectors of the economy.
3. Enhanced Innovation & Technological Advancements:
- Technological Breakthroughs: Renewable energy investment fuels innovation across the sector, leading to:
- More Efficient Technologies: Continuous improvements in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and energy storage technologies drive down costs and improve performance.
- Smart Grid Development: Integrating renewable energy sources into the grid requires advanced smart grid technologies, including smart meters, energy storage systems, and sophisticated control systems. These advancements improve grid stability, reduce energy losses, and enhance efficiency.
- Emerging Technologies: The sector is also seeing growth in areas like floating solar, advanced biofuels, geothermal energy, and concentrated solar power, opening up new possibilities for renewable energy generation.
- Fostering a Knowledge-Based Economy: The transition to renewable energy creates demand for a skilled workforce, promoting education and training in STEM fields. This leads to a more innovative and competitive economy.
- Creating New Industries: The shift to renewable energy necessitates the development of new industries, such as battery manufacturing, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and green hydrogen production.
4. Environmental Benefits & Sustainable Development:
- Reduced Pollution & Healthcare Costs: Renewable energy sources generate little to no air pollution, leading to improved air quality, reduced healthcare costs, and increased worker productivity.
- Combating Climate Change: The primary driver for many investments in renewable energy is the urgent need to mitigate climate change. Transitioning to a low-carbon economy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, helps to limit the impacts of global warming, and supports a more sustainable future.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Renewable energy harnesses naturally replenished resources like sunlight, wind, and water. This reduces dependence on finite fossil fuels and contributes to more sustainable resource management practices.
- Positive Impacts on Tourism and Recreation: Renewable energy projects can contribute to cleaner environments and landscapes, enhancing the attractiveness of tourism and outdoor recreation destinations.
5. Challenges & Considerations:
- Intermittency & Grid Integration: Solar and wind power are intermittent sources, meaning their output fluctuates with weather conditions. Integrating them into the grid requires energy storage solutions, grid modernization, and flexible power plants (e.g., natural gas plants) to provide backup.
- Land Use Conflicts: Large-scale renewable energy projects can compete for land with other uses, such as agriculture and conservation. Careful planning and land use policies are needed to mitigate these conflicts.
- Raw Material Supply Chains: The manufacturing of renewable energy equipment relies on a range of raw materials, including critical minerals. Ensuring secure and sustainable supply chains for these materials is crucial.
- Infrastructure Development: Scaling up renewable energy infrastructure requires significant investment in transmission lines, energy storage, and other supporting infrastructure.
- Policy & Regulatory Support: Supportive government policies, including subsidies, tax incentives, and carbon pricing mechanisms, are essential to accelerate the transition to renewable energy. Stable and predictable regulatory frameworks are needed to attract long-term investment.
- Social Equity and Just Transition: The transition to renewable energy must be equitable, ensuring that the benefits are shared by all communities and that workers in fossil fuel industries have opportunities for retraining and employment in the new economy.
6. Case Studies & Examples:
- China: China is the world’s largest investor and producer of renewable energy, particularly solar and wind. The sector has fueled economic growth, created millions of jobs, and significantly reduced pollution.
- Germany: Germany’s “Energiewende” (energy transition) has transformed its energy system, with renewable energy now supplying a significant share of its electricity. The transition has driven technological innovation, created new industries, and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
- United States: The US is experiencing rapid growth in renewable energy, driven by declining costs, state-level policies, and federal incentives. This has created jobs, spurred investment, and improved energy security.
- India: India has set ambitious targets for renewable energy development, aiming to significantly increase the share of renewables in its energy mix. This is driving economic growth, reducing pollution, and improving energy access.
- Developing Nations in Africa and Latin America: Many developing countries are leveraging their abundant renewable resources, particularly solar and wind, to attract foreign investment, electrify rural communities, and diversify their economies.
Conclusion:
Renewable energy is a powerful driver of economic growth worldwide. Its benefits extend beyond environmental sustainability, encompassing investment, job creation, cost reductions, energy independence, technological innovation, and sustainable development. While challenges remain, the accelerating pace of technological advancements, declining costs, and growing policy support are making the renewable energy transition increasingly inevitable, leading to a cleaner, more prosperous, and secure future for all. Governments, businesses, and individuals must continue to invest in and support the growth of the renewable energy sector to realize its full economic potential. The transition is not just about a shift in power sources; it’s about fundamentally reshaping the global economy for the better.