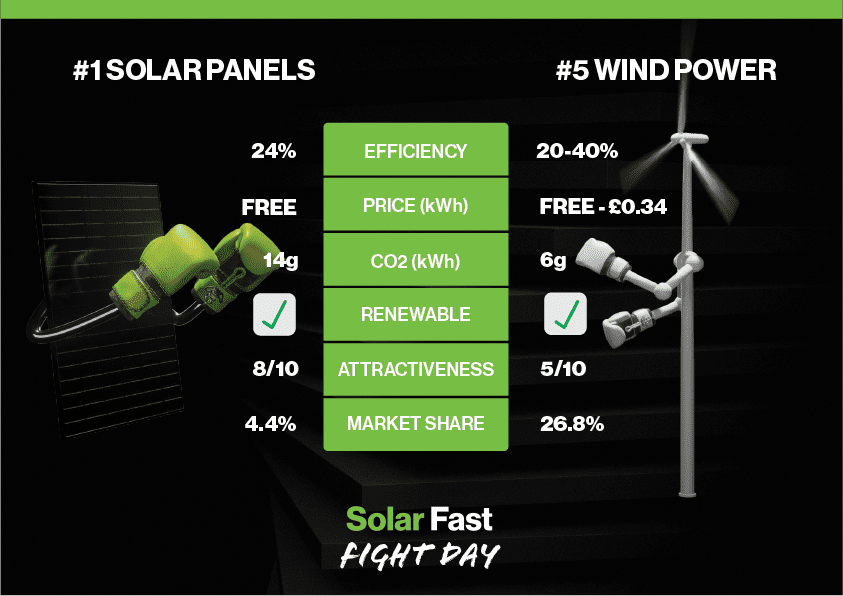
Solar vs. Wind Energy: Which Renewable Reigns Supreme for Your Home?
The future is bright, and it’s powered by sunshine and the breeze. But when it comes to outfitting your home with renewable energy, the question isn’t if, but which. Solar panels and wind turbines – both vying for the title of eco-friendly champion. Let’s dive into a head-to-head comparison, with a dash of creative flair, to help you decide which green energy route is the perfect fit for your castle (or cozy cottage).
The Sun’s Embrace: Solar Power’s Allure
Imagine your roof transforming into a silent sentinel, soaking up the sun’s golden rays and converting them into clean, usable electricity. That, in essence, is solar power in a nutshell. But the beauty of solar extends beyond its simple concept.
The Pros of Solar: Shine On!
- Ubiquitous Resource: The sun shines practically everywhere. Even cloudy locations can generate significant power.
- Simplified Installation: Rooftop solar installations are generally easier and less intrusive than wind turbines.
- Quiet Operation: No whirring blades to disturb your peace. Just clean energy.
- Government Incentives: Solar energy is highly promoted by incentives at every government level
- Resale Value Boost: Homes with solar panels often fetch a higher price on the market.
- Lower Maintenance: Relatively low maintenance requirements and few moving parts.
The Cons of Solar: Cloudy Days and Limitations
- Sun Dependency: No sunshine, no power (without batteries). Nighttime and cloudy days require grid reliance or battery storage.
- Aesthetic Considerations: Panels can sometimes alter the visual appeal of your roof (though sleek designs are becoming more prevalent).
- Space Requirements: Roof space is required, and larger energy needs demand more surface area.
- Initial Cost: Solar system installation typically requires a substantial upfront investment.
Whispers of the Wind: Harnessing Nature’s Breath
Picture a graceful turbine, perched proudly in your yard or on your rooftop, capturing the wind’s energy. While less common than solar, wind power can be a viable option, especially in areas blessed with consistent breezes.
The Pros of Wind: Riding the Wind’s Energy
- Consistent Energy Production: Wind turbines can produce power day and night, even when the sun isn’t shining.
- Potentially Higher Energy Yield: In windy locations, wind turbines can generate a significant amount of electricity, especially in locations that are off-grid.
- Off-Grid Capability: Perfect for isolated properties where grid connection is unavailable or unreliable.
- Environmentally Friendly: Renewable, clean energy.
The Cons of Wind: Battling the Breeze
- Location Dependency: Requires a site with consistent, strong winds. This can be a major hurdle for many homeowners.
- Visual Impact: Wind turbines can be visually intrusive, impacting the aesthetics of your property and neighbor’s views.
- Noise Pollution: Turbines can generate noise, depending on the type and design.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Local regulations regarding wind turbine placement can be complex and restrictive.
- Maintenance: Wind turbines typically require more maintenance compared to solar panels.
- Bird & Wildlife Concerns: Potential impact on bird and bat populations, though mitigation strategies exist.
- Height Limitations: Local ordinances may restrict turbine height.
Head-to-Head Showdown: Solar vs. Wind
Let’s break down the key differences:
| Feature | Solar Power | Wind Power |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Sunlight | Wind |
| Location | Everywhere (with sunlight) | Windy locations |
| Installation | Easier, roof-mounted | More complex, ground or rooftop-mounted |
| Aesthetics | Less noticeable (panel designs improving) | More noticeable (turbine) |
| Noise | Silent | Can be noisy |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Initial high, long-term savings | Initial higher, location-dependent long-term savings |
| Grid Reliance | Night & Cloudy Days: Grid or battery reliance. | Depends on wind availability & storage |
| Environmental Impact | Less | More (noise, wildlife) |
| Durability | Very durable, 25-year warranty. | Durable, but more moving parts. |
The Verdict: Finding Your Energy Match
So, which is the “better” investment? The answer, as with most things, is: it depends.
- For most homeowners: Solar power is generally the more accessible and practical option. Its versatility, ease of installation, and widespread availability of sunlight make it a solid choice.
- If you have a windy location (and the space): Wind power can be a rewarding investment. However, be prepared for more upfront research and planning.
Consider these questions:
- What is your climate? (Sunlight & wind conditions)
- What is your energy consumption? (How much power do you need?)
- What is your budget? (Initial investment, long-term savings)
- What are the local regulations? (Zoning laws, permits)
- What are your personal preferences? (Aesthetics, noise tolerance)
Making the Green Choice: Your Renewable Energy Journey Begins Now
Ultimately, the choice between solar and wind power is a personal one. But no matter which path you choose, you’ll be taking a significant step towards a greener future. Do your research, consult with energy professionals, and prepare to embrace the power of nature. Your home, and the planet, will thank you.

Additional Information
Solar vs. Wind Energy: Which is the Better Investment for Your Home? – A Detailed Analysis
Choosing between solar and wind energy for your home is a decision with significant financial, practical, and environmental implications. It’s not a one-size-fits-all answer, and the “better” investment depends heavily on your specific circumstances. This detailed analysis will delve into the key factors to consider, allowing you to make an informed decision.
I. Key Factors to Consider:
A. Geographical Location & Environmental Factors:
- Sunlight Availability:
- Solar Advantage: This is the most crucial factor for solar. Homes in areas with abundant sunshine throughout the year, particularly in the Southwest, South, and coastal regions, are ideal.
- Wind Advantage: Wind turbine performance is directly linked to wind speed and consistency. Regions with consistently high wind speeds (e.g., coastal areas, plains, hillsides) are best suited. Local wind data analysis is crucial (e.g., using wind maps, anemometers) to assess wind resources.
- Considerations: Cloudy days impact solar panel output significantly. Similarly, wind turbines are less efficient in low wind conditions. Seasonality matters; winter’s shorter days and less sunlight can reduce solar energy production.
- Climate & Weather:
- Solar Considerations: Extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can impact solar panel efficiency. Snow and ice can cover panels and reduce output. Dust, pollen, and debris can also reduce sunlight absorption.
- Wind Considerations: High wind speeds and turbulence can damage wind turbines. Ice buildup on turbine blades can reduce efficiency and pose safety hazards.
- Terrain & Obstructions:
- Solar Considerations: A clear, south-facing roof or open land is ideal for optimal sun exposure. Shade from trees, buildings, or other obstructions will significantly decrease solar panel output.
- Wind Considerations: Turbines require a clear path for wind to flow. Obstructions like trees, buildings, and even large hills can disrupt wind flow and reduce efficiency.
- Zoning Regulations & Local Codes:
- Both Systems: These regulations can significantly impact the feasibility of both solar and wind energy. Local building codes, homeowner association (HOA) restrictions, and zoning laws can limit the size, placement, and aesthetic appearance of installations. Research these regulations thoroughly before investing.
- Wind Considerations: Wind turbines, especially larger ones, often face stricter zoning requirements due to noise concerns, visual impact, and potential hazards (e.g., blade throw).
B. System Costs & Financial Incentives:
- Upfront Costs:
- Solar: The initial investment for solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and installation can be substantial. However, prices have decreased significantly in recent years.
- Wind: Wind turbines generally have a higher upfront cost than solar panel systems, especially for residential-scale turbines. This includes the turbine itself, tower, installation, and maintenance infrastructure.
- Considerations: Cost depends on system size (kW), type of panels/turbine, brand, and installer. Get multiple quotes from qualified professionals.
- Operating & Maintenance Costs:
- Solar: Solar panels have minimal moving parts and require relatively low maintenance. Cleaning panels periodically and occasional inverter replacement are typical costs.
- Wind: Wind turbines have moving parts, requiring regular maintenance, inspections, and potential component replacements (e.g., gearboxes, blades). Preventative maintenance is crucial to extend lifespan.
- Considerations: Factor in these ongoing costs when calculating the long-term economic benefits.
- Financial Incentives & Rebates:
- Both Systems: Government incentives (federal tax credits), state rebates, and local programs can significantly reduce the upfront cost of both solar and wind energy.
- Considerations: Research available incentives in your area. These can change over time, so stay informed.
- Net Metering & Feed-In Tariffs:
- Both Systems: These programs allow homeowners to sell excess electricity generated back to the grid, reducing electricity bills.
- Considerations: The availability and compensation rates of these programs vary by location. They greatly impact the payback period and profitability of the systems.
- System Lifetime & Warranty:
- Solar: Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25-30 years and come with warranties guaranteeing output over time.
- Wind: Wind turbines usually have a lifespan of 20-25 years, but this depends heavily on maintenance. Warranties cover performance and component failures.
- Considerations: Longer warranties and system lifespans translate to greater long-term value.
C. Energy Needs & Consumption Habits:
- Household Energy Consumption:
- Both Systems: The size of the solar panel or wind turbine system should be tailored to your household’s energy consumption. Larger energy demands require larger (and more expensive) systems.
- Considerations: Analyze your past electricity bills to understand your average daily and annual energy usage (kWh).
- Load Profile (Energy Usage Patterns):
- Solar Advantage (Sometimes): Solar energy production aligns well with daytime energy consumption for many households, especially those with peak usage during the day.
- Wind Advantage (Sometimes): Wind can generate energy throughout the day and night, making it potentially more suitable for households with constant energy demands.
- Considerations: If your energy consumption is high at night (e.g., electric vehicle charging, operating appliances), a battery storage system in conjunction with either solar or wind becomes more attractive.
- Energy Storage (Batteries):
- Both Systems: Adding a battery storage system can store excess energy generated during peak production periods (solar during the day, wind during windy periods) for use during times when production is lower or when the grid is down.
- Considerations: Battery systems add significant upfront cost but can provide increased energy independence and resilience to grid outages.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Both Systems: Investing in energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and other home improvements will reduce your overall energy demand and make any renewable energy system more effective and economical.
D. Space & Aesthetics:
- Space Requirements:
- Solar: Solar panels require sufficient roof space or land area free from shade.
- Wind: Wind turbines, especially larger ones, require a significant amount of land for the tower, rotor clearance, and safety zones.
- Considerations: Evaluate available space and the potential visual impact.
- Aesthetics & Visual Impact:
- Both Systems: Some homeowners are concerned about the aesthetics of solar panels on their roofs or wind turbines in their yards.
- Considerations: Consider the appearance of the systems and their impact on property values. Solar panels can be integrated into roof designs, and turbine designs are constantly evolving.
- Noise:
- Wind: Wind turbines can produce noise, which can be a concern, especially for residential-scale turbines.
- Considerations: Check local noise ordinances. Ensure that the turbine is located far enough from your home and neighbors to minimize noise pollution.
II. Comparative Analysis (Solar vs. Wind):
| Feature | Solar Energy | Wind Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Sun-rich areas, clear skies, south-facing roofs | Windy areas, open terrain, less obstructed wind flow |
| Upfront Cost | Lower, especially with incentives | Higher, especially for residential-scale turbines |
| Operating Costs | Low, minimal maintenance | Higher, regular maintenance & component replacement |
| Energy Production | Primarily during daylight hours | Day and night, subject to wind availability |
| Space Requirements | Roof space or land area for panels | Land area for turbine, tower, safety zone |
| Aesthetics | Can be integrated into roofs, varies | Often more visually prominent |
| Noise | Quiet | Can produce noise, depending on turbine design |
| Regulatory | Less complex, depends on local codes | More complex, zoning restrictions are common |
| Performance | Affected by cloud cover, seasons | Affected by wind speed, turbulence, and obstacles |
| Energy Independence | Significant, especially with battery storage | Significant, especially with battery storage |
III. Making the Decision:
A. Assessment Process:
- Energy Needs & Usage: Analyze your electricity bills to determine your average energy consumption and peak usage times.
- Site Assessment: Evaluate your property’s suitability for solar and wind. Assess sunlight availability, wind resources (if considering wind), and potential obstructions.
- Local Research: Research zoning regulations, homeowner association restrictions, and available financial incentives.
- Get Professional Quotes: Obtain quotes from reputable installers for both solar and wind systems, considering all costs, incentives, and performance estimates.
- Financial Analysis: Conduct a detailed financial analysis, including the initial investment, operating costs, energy savings, potential revenue from net metering, and estimated payback period.
- Consider Long-Term Goals: Evaluate your long-term energy goals, including energy independence, environmental impact, and potential property value enhancement.
B. Choosing the Right Option:
- Solar is Often the Better Starting Point for Most Homeowners: Due to decreasing costs, simpler installation, lower maintenance, and fewer regulatory hurdles, solar is often the more accessible and economically viable option for most homeowners.
- Wind May Be a Good Option in Specific Circumstances: If you live in a consistently windy area with suitable land availability and can overcome zoning restrictions, wind energy can provide a significant source of renewable energy.
- Consider a Hybrid Approach: In some situations, a combination of solar and wind can maximize renewable energy generation and energy independence. However, this approach will increase upfront costs and require careful integration of the systems.
- Prioritize Energy Efficiency: Before investing in any renewable energy system, prioritize energy efficiency measures in your home. Reducing your energy consumption will make any renewable energy system more effective and cost-efficient.
IV. Conclusion:
Choosing between solar and wind energy is a multifaceted decision. There is no single “better” investment. It depends on your location, your property, your energy needs, and your financial considerations. By conducting a thorough assessment, researching local regulations and incentives, and comparing quotes from qualified professionals, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your goals and maximizes the benefits of renewable energy for your home. Remember to consider not just the immediate financial costs, but also the long-term environmental impact and the potential for increased energy independence.