Why Green Data Centers Are Key to Reducing Global Emissions
The digital world hums with invisible energy. From streaming cat videos to complex financial transactions, all of it runs on data – and that data lives in data centers. These colossal warehouses are the digital lungs of our connected age, but they also have a significant carbon footprint. The good news? Green data centers offer a powerful solution to reduce global emissions, shifting our digital dependence towards a sustainable future.
The Energy Hog: Data Centers’ Carbon Shadow
Let’s face it: traditional data centers are energy hogs. They gobble up electricity like Pac-Man on steroids. This energy fuels servers, cooling systems, and a constant flow of data. The problem? Much of this energy is generated from fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Here’s a bite-sized reality check:
| Data Center Demand (Current) | Energy Equivalent |
|---|---|
| ~1-2% of Global Electricity Usage | Equivalent to a small nation’s consumption |
Beyond the Bytes: The Green Data Center Revolution
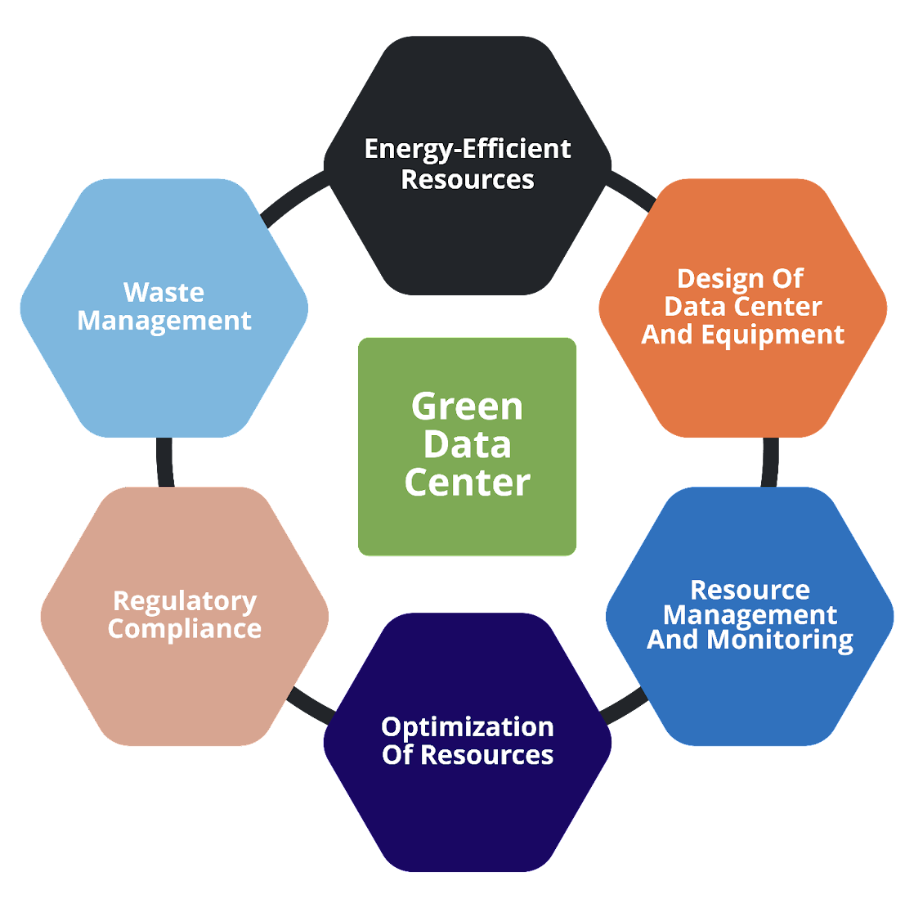
A green data center is more than just a building; it’s an ecosystem designed for efficiency and sustainability. It prioritizes energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and waste reduction strategies. This transforms them from carbon contributors to climate champions.
Key Features of Green Data Centers:
- Renewable Power: Powered by solar, wind, and hydro, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Efficient Cooling: Employing innovative cooling techniques like free cooling (using outside air) and liquid cooling to minimize energy consumption.
- Server Optimization: Utilizing virtualization, efficient servers, and AI-powered energy management to reduce power usage.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing recycling programs and responsibly disposing of electronic waste (e-waste).
- Building Design: Constructing buildings with energy-efficient materials and designs.
Freeing Up the Air: Emission Reduction Benefits
The impact of green data centers on global emissions is substantial.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By utilizing renewable energy and implementing energy-efficient technologies, these centers significantly lower their carbon emissions.
- Lowering the Cost: Over time the efficiency pays off and the energy bill is significantly lower.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Encouraging a shift towards eco-conscious operations within the tech industry.
Let’s put some numbers to the power:
| Impact Metric | Green Data Center Advantage |
|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Significantly reduced |
| Energy Consumption | Optimized |
| Water Usage | Optimized |
The Path Forward: Embracing a Greener Future
The transition to green data centers isn’t just an environmental imperative; it’s also economically and socially beneficial. Investing in sustainable infrastructure creates jobs, fosters innovation, and enhances a company’s brand image.
Taking Action:
- Government Incentives: Policy makers need to encourage data centers to go green.
- Industry Collaboration: Tech companies, governments, and organizations need to work together.
- Consumer Demand: Consumers can drive change by choosing eco-conscious services.
By choosing green, we not only ensure a more sustainable digital world but also help protect the planet for future generations. The time to act is now.

Additional Information
Green Data Centers: A Deep Dive into Reducing Global Emissions
Green data centers, also known as sustainable or energy-efficient data centers, are critical to reducing global emissions for a multitude of interconnected reasons. They represent a proactive and increasingly necessary response to the burgeoning energy demands of the digital age and the urgent need to mitigate climate change. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. The Growing Energy Consumption of Data Centers:
- Exponential Growth: The digital world is expanding at an unprecedented rate. Cloud computing, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and the proliferation of online services (streaming, gaming, social media) all rely heavily on data centers. This leads to a relentless increase in demand for processing power and storage capacity.
- Electricity Hogging: Data centers are incredibly energy-intensive. They consume vast amounts of electricity for:
- Servers: The core processing units require constant power.
- Cooling: Servers generate significant heat, necessitating sophisticated and energy-guzzling cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Networking Equipment: Routers, switches, and other network infrastructure require continuous power.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs) & Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): These systems ensure a stable and continuous power supply, consuming additional energy.
- Global Impact: Data centers already account for a significant and growing percentage of global electricity consumption (estimated at around 1-2% currently, but projected to rise significantly). This translates into a substantial carbon footprint, particularly as much of the electricity currently comes from fossil fuels.
2. The Carbon Footprint of Data Centers:
- Direct Emissions (Scope 1): These come from on-site combustion of fuels, such as generators for backup power.
- Indirect Emissions (Scope 2): These are primarily from the electricity used to power the data center. The carbon intensity of this electricity depends on the energy sources used by the local grid (e.g., coal, natural gas, renewable energy).
- Value Chain Emissions (Scope 3): These are the most complex and encompass a wide range of emissions, including:
- Manufacturing of Hardware: The production of servers, networking equipment, and cooling systems is energy-intensive and relies on materials with significant environmental impacts.
- Transportation of Equipment: Shipping hardware to data centers contributes to carbon emissions.
- Construction of Data Center Facilities: Building data centers requires significant concrete, steel, and other materials that have high embodied carbon.
- Waste Disposal: The disposal of obsolete hardware, which is often sent to landfills, contributes to environmental pollution.
- Employee Commuting and Business Travel: The operation of a data center necessitates employee travel and other business activities, contributing to emissions.
3. Key Strategies for Green Data Centers and Emission Reduction:
Green data centers employ various strategies to minimize energy consumption and reduce their carbon footprint:
- Energy-Efficient Hardware:
- Server Optimization: Choosing servers with high energy efficiency ratings (e.g., Energy Star certified) and optimizing server utilization (e.g., virtualization, consolidation) can significantly reduce power consumption.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): SSDs consume less power than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and offer improved performance.
- Power Supply Units (PSUs): Using highly efficient PSUs with high 80 Plus certification minimizes energy waste.
- Efficient Cooling Systems:
- Free Cooling: Leveraging natural cooling methods like outside air (if climate permits) or water-based cooling systems (e.g., using cold lake or river water) can drastically reduce the need for energy-intensive mechanical cooling.
- Liquid Cooling: Immersing servers directly in liquid coolants offers highly efficient heat removal.
- Hot/Cold Aisle Containment: This helps to direct the flow of cool and hot air, preventing mixing and improving cooling efficiency.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Controlling the speed of cooling fans allows for more efficient cooling based on real-time demand.
- Renewable Energy Sources:
- On-site Solar Power: Installing solar panels on the roof or surrounding land can generate clean electricity directly for the data center.
- Wind Energy: Partnering with wind farms or purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs) helps to offset the carbon footprint.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Long-term contracts with renewable energy providers guarantee a supply of clean electricity.
- Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE):
- Monitoring and Optimization: PUE is a metric used to measure the energy efficiency of a data center, calculated by dividing the total power used by the data center by the power used by the IT equipment. Striving for lower PUE values (closer to 1.0) is a key goal.
- Advanced Metering and Monitoring: Implementing advanced monitoring systems helps to track energy consumption in real-time and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Center Design and Location:
- Strategic Location: Choosing locations with favorable climates (e.g., cooler temperatures) and access to renewable energy sources can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Modular Design: Building data centers in modular units allows for scalable expansion and reduces the risk of overbuilding.
- Building Materials: Using sustainable and energy-efficient building materials (e.g., recycled content, low-emission materials) minimizes embodied carbon in the data center construction.
- Virtualization and Cloud Computing:
- Consolidation: Virtualization allows for the consolidation of multiple workloads onto fewer servers, reducing the overall hardware footprint and energy consumption.
- Cloud Migration: Migrating workloads to public cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) can often result in greater energy efficiency due to economies of scale, optimized infrastructure, and access to renewable energy investments. However, it’s important to vet the cloud provider’s sustainability practices.
- Waste Management:
- Hardware Recycling and Reuse: Implementing a robust hardware recycling program helps to minimize waste and conserve resources. Refurbishing and reusing older hardware can also extend its lifecycle.
- E-waste Management: Ensuring that all electronic waste is properly managed and disposed of through responsible channels prevents environmental pollution.
- Carbon Offsetting:
- Carbon Credits: Investing in carbon offset projects (e.g., reforestation, renewable energy projects) can compensate for unavoidable emissions. This is a crucial step while transitioning to green data centers.
- Powering Up the IT Efficiency:
- Green Coding Practices: Optimizing code to reduce processing, memory requirements, and network usage can significantly reduce the energy consumed by the applications and services.
- Server Utilization: This means making sure servers are used to their full capacity, so that they are less idle, and not consuming energy for nothing.
4. The Benefits of Green Data Centers:
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The primary and most significant benefit is the substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to mitigating climate change.
- Lower Energy Costs: Energy-efficient practices translate into lower electricity bills, significantly reducing operational expenses.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Optimized infrastructure and improved monitoring systems lead to greater overall efficiency.
- Improved Reliability and Uptime: Implementing advanced cooling and power systems enhances the reliability and availability of data center operations.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Adopting green practices demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, which can enhance brand image and attract environmentally conscious customers and investors.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many governments and organizations are enacting regulations and standards related to energy efficiency and carbon emissions, making green data centers crucial for compliance.
- Resource Conservation: Reducing energy consumption translates into conserving valuable natural resources and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Employees, particularly younger generations, are increasingly attracted to companies with strong sustainability commitments.
5. Challenges and Barriers:
- Upfront Investment Costs: Implementing green technologies can require a significant initial investment in new hardware, software, and infrastructure upgrades.
- Technology Complexity: Designing, implementing, and managing green data centers can be technically complex, requiring specialized expertise.
- Data Center Retrofits: Retrofitting existing data centers to incorporate green technologies can be challenging and expensive.
- Grid Infrastructure: The availability of renewable energy sources and the capacity of the local grid to handle increased renewable energy generation can be limiting factors.
- Lack of Standardization: A lack of standardized metrics and certification programs can make it challenging to assess and compare the sustainability performance of different data centers.
- Balancing Performance and Efficiency: Finding the optimal balance between energy efficiency and performance requirements can be a complex balancing act.
6. The Future of Green Data Centers:
The future of green data centers is bright and promising. Here are some trends and developments to watch:
- Increased Adoption of Renewable Energy: The cost of renewable energy technologies (solar, wind) is declining rapidly, making them increasingly cost-competitive with fossil fuels.
- Advanced Cooling Technologies: Continued innovation in cooling technologies, such as liquid cooling, is expected to further improve energy efficiency.
- AI-powered Optimization: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play a key role in optimizing data center operations, including energy consumption, cooling, and server utilization.
- Data Center as a Service (DCaaS): This model allows organizations to outsource their data center needs to specialized providers, often with built-in energy-efficient infrastructure and operational practices.
- Circular Economy Principles: Data centers will increasingly adopt circular economy principles, focusing on reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of hardware.
- Increased Government Regulations and Incentives: Governments are likely to impose stricter regulations and offer incentives to promote energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): In the long term, CCS technologies could play a role in capturing carbon emissions from data centers that use fossil fuel-based backup generators.
Conclusion:
Green data centers are not just a trend; they are a necessity for a sustainable future. By implementing a range of energy-efficient technologies, utilizing renewable energy sources, and adopting responsible operating practices, data centers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to mitigating climate change. The transition to green data centers is essential to support the continued growth of the digital economy while minimizing its environmental impact. Collaboration between data center operators, technology providers, governments, and consumers is crucial to accelerate this transition and ensure a cleaner, more sustainable future for everyone.